Parse tree design
From CSSEMediaWiki
(Difference between revisions)
(→1st Design) |
|||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
That's the first Design that came up in class. It is a [[Composite]] Pattern. | That's the first Design that came up in class. It is a [[Composite]] Pattern. | ||
*the addKid()-function in the Terminal class throws an exception | *the addKid()-function in the Terminal class throws an exception | ||
| − | *symbol is of type enum, which has a representation for every symbol of the grammar. | + | *symbol is of type [[Enum idiom|enum]], which has a representation for every symbol of the grammar. |
Problem: [[Beware type switches|Beware of Typeswitch]] | Problem: [[Beware type switches|Beware of Typeswitch]] | ||
Revision as of 21:13, 6 October 2008
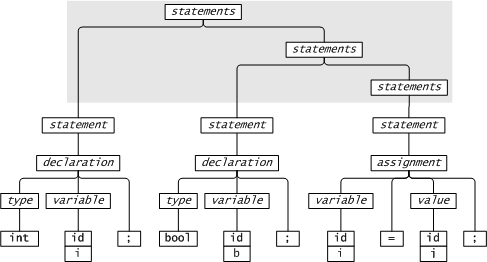
A context free grammar defines a language, e.g.
A parse tree shows how a sentence in the language is structured according to the grammar.
Contents |
Terminology
In parsing lingo a symbol is a name in a grammar. Each symbol is either a terminal or a non-terminal. Non-terminals appear on the left hand side of a grammar production; terminals don't.
Class-Design
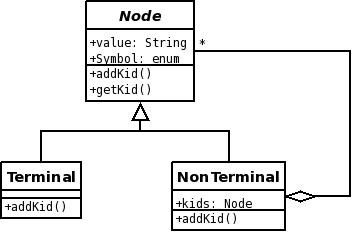
1st Design
That's the first Design that came up in class. It is a Composite Pattern.
- the addKid()-function in the Terminal class throws an exception
- symbol is of type enum, which has a representation for every symbol of the grammar.
Problem: Beware of Typeswitch
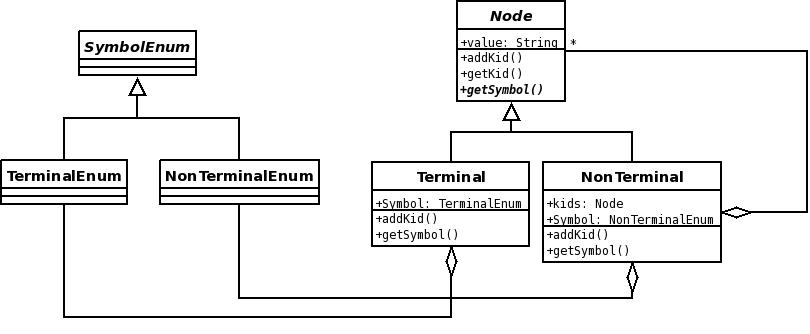
2nd Design
To overcome the Beware of Typeswitch problem an enum-hierarchy was added, so that a NonTerminal Symbol cannot have a Terminal Symbol.