Interpreter
JaninaVoigt (Talk | contribs) (→Structure) |
JaninaVoigt (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
===Client=== | ===Client=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Consequences== | ||
| + | *Interpreter makes it easy to change and extend the grammar using inheritance. | ||
| + | *Implementing the grammar is easy because the nodes in the abstract syntax tree have similar interpretations are are usually easy to write. Often, writing these classes can be automated using a compiler or parser generator. | ||
| + | *It is hard to maintain complex grammar using Interpreter because it defines at least one class for every rule in the grammar. This can soon lead to a huge number of classes. | ||
| + | *It is easy to add new ways to interpret an expression. | ||
== Related Patterns == | == Related Patterns == | ||
Revision as of 02:22, 25 July 2009
The interpreter pattern is specific implimentation of the composite pattern generally used for language parsing. In the interpreter pattern a class is produced for each symbol in the language. A statement can then be broken down into a syntax tree of these classes which can in turn be used to interpret the statement.
Contents |
Use When
You should use Interpreter when there is a language that you need to interpret and when the statements of the language can be represented as abstract syntax trees. It works best when:
- the grammar of the language is simple. Otherwise, the class hierarchy for the grammar becomes large and complex.
- efficiency is not essential.
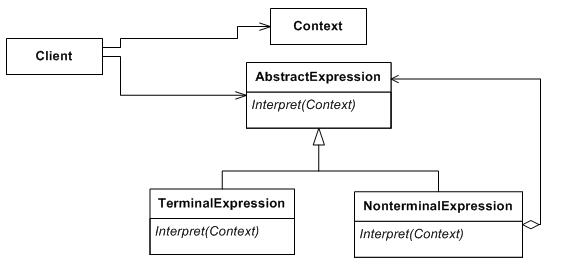
Structure
(from wikipedia)
Participants
Abstract Expression
Terminal Expression
Nonterminal Expression
Context
Client
Consequences
- Interpreter makes it easy to change and extend the grammar using inheritance.
- Implementing the grammar is easy because the nodes in the abstract syntax tree have similar interpretations are are usually easy to write. Often, writing these classes can be automated using a compiler or parser generator.
- It is hard to maintain complex grammar using Interpreter because it defines at least one class for every rule in the grammar. This can soon lead to a huge number of classes.
- It is easy to add new ways to interpret an expression.
Related Patterns
- Composite: The abstract syntax tree uses a Composite pattern.
- Flyweight: This pattern can be used to share the terminal symbols.
- Iterator: This pattern can be used to traverse the Interpreter structure.
- Visitor: This pattern can be used to collect the behavior for all abstract syntax tree nodes in one class.
| Design patterns | |
|---|---|
|
Creational: Abstract Factory | Builder | Factory Method | Prototype | Singleton | |