Parse tree design
From CSSEMediaWiki
(Difference between revisions)
WarwickIrwin (Talk | contribs) m (Removed last year's efforts) |
|||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
== Terminology == | == Terminology == | ||
In parsing lingo a ''symbol'' is a name in a grammar. Each symbol is either a ''terminal'' or a ''non-terminal''. Non-terminals appear on the left hand side of a grammar production; terminals don't. | In parsing lingo a ''symbol'' is a name in a grammar. Each symbol is either a ''terminal'' or a ''non-terminal''. Non-terminals appear on the left hand side of a grammar production; terminals don't. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Issues Discussed == | ||
| + | Around this design we constructed a variety of patterns and discussed them. | ||
| + | === Patterns in Use === | ||
| + | * DTSTTCPW Design | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Downcasting vs No-ops vs [[DBC]] based superclasses === | ||
| + | === Data Redundancy === | ||
| + | === Test Driven Development & Refactoring === | ||
| + | |||
| + | == See Also == | ||
| + | * [[Avoid no-ops]] | ||
| + | * [[Beware type switches]] | ||
| + | * [[Decorator]] | ||
| + | * [[Refactoring]] | ||
Revision as of 03:19, 6 August 2009
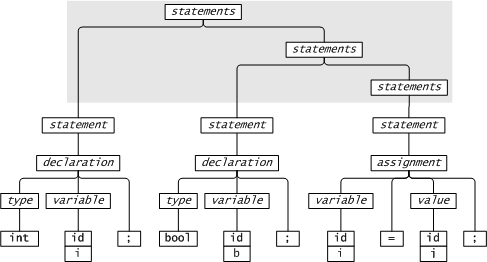
A context free grammar defines a language, e.g.
A parse tree shows how a sentence in the language is structured according to the grammar.
Contents |
Terminology
In parsing lingo a symbol is a name in a grammar. Each symbol is either a terminal or a non-terminal. Non-terminals appear on the left hand side of a grammar production; terminals don't.
Issues Discussed
Around this design we constructed a variety of patterns and discussed them.
Patterns in Use
- DTSTTCPW Design