Command
Tanmay Bhola (Talk | contribs) (→Invoker (MenuItem)) |
|||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
*creates a ConcreteCommand object and sets its receiver. | *creates a ConcreteCommand object and sets its receiver. | ||
===Invoker (MenuItem)=== | ===Invoker (MenuItem)=== | ||
| − | *asks the command to carry out the request. | + | *asks the command to carry out the request. This is done by calling the execute() method. |
| + | |||
===Receiver (Document, Application)=== | ===Receiver (Document, Application)=== | ||
*knows how to perform the operations associated with carrying out a request. Any class may serve as a Receiver. | *knows how to perform the operations associated with carrying out a request. Any class may serve as a Receiver. | ||
Revision as of 01:15, 7 April 2010
In the Command pattern objects are used to represent actions. An action and its parameters are encapsulated by a command object.
Contents |
Usage
Sometimes you need to issue a request to an object without even knowing anything about the requested operation or the receiving object itself, then it is useful to apply the Command pattern. A situation where to use the Command pattern would be for example the implementation of a menu in a GUI. Every single menu item has its own corresponding concrete command object, which implement a command interface. When the user clicks on a menu item the menu item calls the execute() method of its command object. The execute() method carries out an operation. The concrete commands store the receiver and call up one or more operations on the receiver. Good examples for menu items would be the opening and closing of documents or also pasting some text. Another example would be a PrintJob where PrintCommand objects set the properties (the document to be printed, the number of copies, and so on), and finally call a method to send the job to the printer. Other applications include undo operations, GUI buttons, networking and parallel processing.
The Command pattern has the following advantages:
- a command object is a convenient place to collect code and data related to a specific action
- treating commands as objects supports undo-able operations, provided that the command objects are stored (eg in a stack)
- the construction of a command and the actual execution of that command can happen at different times
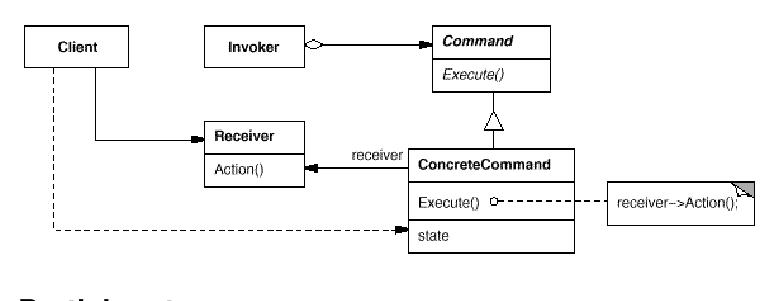
UML Diagram
Participants
Command
- declares an interface for executing an operation.
ConcreteCommand (PasteCommand, OpenCommand)
- defines a binding between a Receiver object and an action.
- implements Execute by invoking the corresponding operation(s) on Receiver.
Client (Application)
- creates a ConcreteCommand object and sets its receiver.
Invoker (MenuItem)
- asks the command to carry out the request. This is done by calling the execute() method.
Receiver (Document, Application)
- knows how to perform the operations associated with carrying out a request. Any class may serve as a Receiver.
Consequences
- Command decouples the object that invokes the command from the object that responds to the command.
- Commands can be extended and manipulated like other objects.
- You can assemble commands into composite commands using the Composite pattern.
- It's easy to add new commands because existing classes won't be affected by the change.
Related Patterns
- Composite: This pattern can be used to implement composite commands.
- Memento: This pattern can be used to keep the state required to undo a command's effect.
- Prototype: Sometimes a command can be copied before being placed in the command history. In this case, the original command can act like a prototype that is copied.
| Design patterns | |
|---|---|
|
Creational: Abstract Factory | Builder | Factory Method | Prototype | Singleton | |