Parse tree design
From CSSEMediaWiki
(Difference between revisions)
(Removed old stuff) |
|||
| (4 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
== Terminology == | == Terminology == | ||
In parsing lingo a ''symbol'' is a name in a grammar. Each symbol is either a ''terminal'' or a ''non-terminal''. Non-terminals appear on the left hand side of a grammar production; terminals don't. | In parsing lingo a ''symbol'' is a name in a grammar. Each symbol is either a ''terminal'' or a ''non-terminal''. Non-terminals appear on the left hand side of a grammar production; terminals don't. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 01:44, 11 August 2010
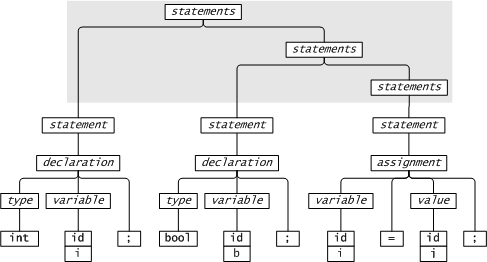
A context free grammar defines a language, e.g.
A parse tree shows how a sentence in the language is structured according to the grammar.
Terminology
In parsing lingo a symbol is a name in a grammar. Each symbol is either a terminal or a non-terminal. Non-terminals appear on the left hand side of a grammar production; terminals don't.