Singleton
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
* If you're using the static nature of the pattern to avoid passing around many references, it's a sign you might be overusing that class, and not following the maxim of [[Tell, don't ask]]. Possibly you have a [[Avoid god classes|God class]]. It's a sign that you should at least think about restructuring the code to reduce dependence on this class. | * If you're using the static nature of the pattern to avoid passing around many references, it's a sign you might be overusing that class, and not following the maxim of [[Tell, don't ask]]. Possibly you have a [[Avoid god classes|God class]]. It's a sign that you should at least think about restructuring the code to reduce dependence on this class. | ||
* You don't need a Singleton to make use of [[Use lazy initialization pattern|lazy initialization]]. If you're using a Singleton just for this, then you definitely need to get rid of it. | * You don't need a Singleton to make use of [[Use lazy initialization pattern|lazy initialization]]. If you're using a Singleton just for this, then you definitely need to get rid of it. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Related Patterns == | ||
| + | Many patterns can be implemented using the Singleton pattern. See [[Abstract Factory]], [[Builder]], and [[Prototype]]. | ||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
* [[Design patterns]] | * [[Design patterns]] | ||
* [[No global variables]] | * [[No global variables]] | ||
| − | |||
Revision as of 05:29, 7 October 2008
Singleton is a simple design pattern to ensure that only one instance of a class can exist, and provide an easy, global way to access it. Some classes in a domain should only ever have one instance, for example a Printer Spooler class that handles print requests and sends them to Printers. A global variable could be used, but this is bad design and doesn't stop multiple instances being created.
The Singleton pattern makes the class itself responsible for ensuring only one instance exists.
Contents |
Use when
- There must be only one instance of a class and it must be easily accessible to clients.
- When the class needs to be extensible, and clients should be able to use a derived class without changing their code.
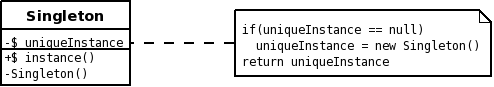
Structure
Singleton defines an instance() method through which clients can access the unique instance. If an instance doesn't exist, it creates one before returning it. The constructor is private, ensuring only one instance can be created. The $ signs mean "static."
Recognising the pattern
Classes: Singleton.
- private constructor.
- private static attribute to hold uniqueInstance of itself.
- concrete public static getInstance() method.
Risks of Singleton
The Singleton design pattern has several apparent advantages. The programmer can be sure that only one instance will exist. That instance is static. This saves the mess of having to pass around many references to the object. Also, lazy initialization is an inherent part of the pattern, which can improve performance.
However, these advantages can tempt the programmer to make unwise design decisions.
- The assumption that only one instance will ever be required can be shortsighted. For example, one may have a Settings object as a singleton. But if one later wishes to extend the software to run multiple objects each with their own Settings instance, much painstaking refactoring will be required.
- If you're using the static nature of the pattern to avoid passing around many references, it's a sign you might be overusing that class, and not following the maxim of Tell, don't ask. Possibly you have a God class. It's a sign that you should at least think about restructuring the code to reduce dependence on this class.
- You don't need a Singleton to make use of lazy initialization. If you're using a Singleton just for this, then you definitely need to get rid of it.
Related Patterns
Many patterns can be implemented using the Singleton pattern. See Abstract Factory, Builder, and Prototype.