Frogs second design
From CSSEMediaWiki
(Difference between revisions)
(Singleton) |
m (→Design notes) |
||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
* A Toad can masquerade as a Frog, because Igor can’t tell the difference. FakeFrog makes a Toad conform to the type of Frog. | * A Toad can masquerade as a Frog, because Igor can’t tell the difference. FakeFrog makes a Toad conform to the type of Frog. | ||
* Igor doesn’t eat Frogs any more, ever since he accidentally ate a Toad. | * Igor doesn’t eat Frogs any more, ever since he accidentally ate a Toad. | ||
| − | * A | + | * A RealFrog can advancePhase() from an Egg to a Tadpole to an Adult to Dead by changing its Phase object. |
* Phase objects are provided by a PhaseSelector. For every tadpole or adult Frog. | * Phase objects are provided by a PhaseSelector. For every tadpole or adult Frog. | ||
* PhaseSelector makes one Tadpole or Adult phase object. However, it uses a single Egg instance and a single Dead instance for all Frogs, because these two Phases don't need any data except birthDay and deathDay, which can be retrieved from Frog. | * PhaseSelector makes one Tadpole or Adult phase object. However, it uses a single Egg instance and a single Dead instance for all Frogs, because these two Phases don't need any data except birthDay and deathDay, which can be retrieved from Frog. | ||
Revision as of 10:59, 23 September 2009
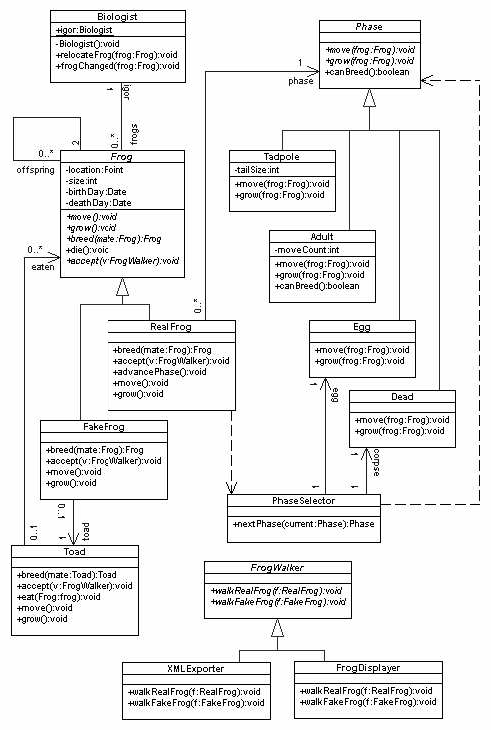
Another OO model of frogs. This design appeared in the 2006 427 exam.
Design notes
Following criticism of the Frogs Design, the designer has studied design patterns and tried again.
- As before, this design models the lifecycles of Frogs.
- Getters and setters are omitted from the diagram, but may be assumed where necessary.
- There is one Biologist, Igor, who manages the Frogs. Igor moves around as required for experiments.
- There are many Frogs. The design minimises Frogs' knowledge of each other, instead using Igor to coordinate Frog behaviour. Whenever a Frog changes state, it tells Igor by calling frogChanged(), and Igor may choose to move() Frogs, or tell them to grow(), breed(), etc.
- A Toad can masquerade as a Frog, because Igor can’t tell the difference. FakeFrog makes a Toad conform to the type of Frog.
- Igor doesn’t eat Frogs any more, ever since he accidentally ate a Toad.
- A RealFrog can advancePhase() from an Egg to a Tadpole to an Adult to Dead by changing its Phase object.
- Phase objects are provided by a PhaseSelector. For every tadpole or adult Frog.
- PhaseSelector makes one Tadpole or Adult phase object. However, it uses a single Egg instance and a single Dead instance for all Frogs, because these two Phases don't need any data except birthDay and deathDay, which can be retrieved from Frog.
- A Frog can breed() to make offspring of the appropriate type.
- Tasks such as exporting XML and displaying Frog information are separated into FrogWalket subclasses. A Frog object can accept() a FrogWalker and call the WalkRealFrog() or WalkFakeFrog() method as appropriate for that Frog. It then tells offspring Frogs to accept the FrogWalker.
GoF Design Patterns
- Observer - Biologist observes Frog.
- State - Phase.
- Adapter - FakeFrog.
- Visitor - FrogWalker.
- Singleton - Biologist