Warfarin Design
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
* Main use case is to record a new blood test (INR reading), get a dose prediction. | * Main use case is to record a new blood test (INR reading), get a dose prediction. | ||
* Dose predictions may be returned in several ways, probably not advisable to just give the dose to prescribe because of liability issues. For example, could give a graphical representation of the likelihood of being below the safe range, in range or above. | * Dose predictions may be returned in several ways, probably not advisable to just give the dose to prescribe because of liability issues. For example, could give a graphical representation of the likelihood of being below the safe range, in range or above. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
* The system needs to be able to "learn" a model from the historical data. This involves transforming the data into a special format (an "ARFF" file) and submitting this to the learning algorithm. | * The system needs to be able to "learn" a model from the historical data. This involves transforming the data into a special format (an "ARFF" file) and submitting this to the learning algorithm. | ||
* The data-to-arff step needs to be flexible (i.e. able to be easily changed if the learner's data requirements change. | * The data-to-arff step needs to be flexible (i.e. able to be easily changed if the learner's data requirements change. | ||
* Models will need to be persisted. | * Models will need to be persisted. | ||
* The data needs to be reliably persisted. | * The data needs to be reliably persisted. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | == | + | == Future requirements == |
| − | + | * There may be a need to record other data for the patient, possibly temporally, such as diet, other drugs taken, smoking and alcohol consumption. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | == Initial design == | |
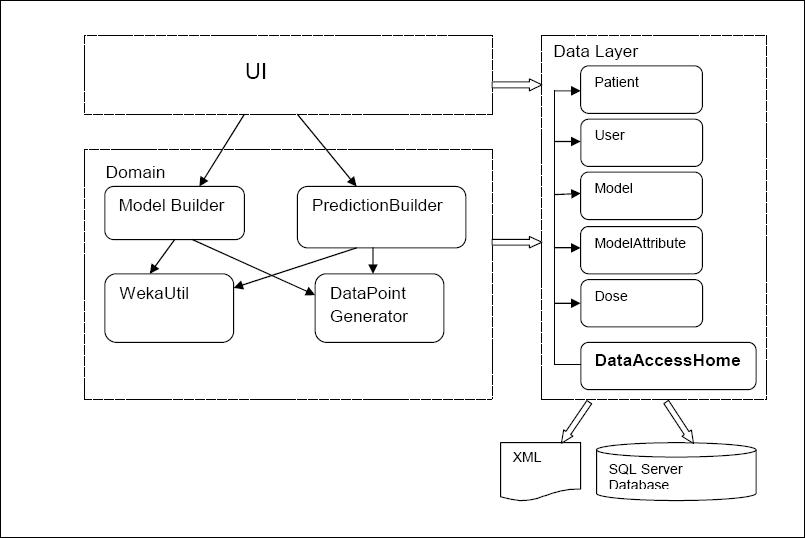
The high level design: | The high level design: | ||
[[image:WarfarinArc.JPG|frame|left|]] | [[image:WarfarinArc.JPG|frame|left|]] | ||
Revision as of 12:17, 29 July 2010
Contents |
Background
Warfarin predictor was a result of my cosc366 research project. It is a web based application that uses machine learning algorithms to predict a right dose for hart-valve transplant patients. The importance of determining a correct dose comes from a fact that there is a very real danger of blood clots occurring on the heart-valve of a patient . In order to prevent blood clotting Warfarin is taken by patients as a blood thinner. By taking a right dose a patient has a minimal chance of clotting, while still ensuring that patient has enough clotting ability so that he or she does not bleed to death.
Even though I did try to do this project in OO style, the functionality that needed to come out of it were more important for the project so I haven’t spent too much time on putting it in right OO space. There is a good chance I will need to work on this project again ( add some more functionality) in the near future so before I do start I would like to see it being refactored.
Initial Requirements
- System users: administrators, doctors.
- Administrators can add new doctors.
- Doctors adds patients, patient records.
- Main use case is to record a new blood test (INR reading), get a dose prediction.
- Dose predictions may be returned in several ways, probably not advisable to just give the dose to prescribe because of liability issues. For example, could give a graphical representation of the likelihood of being below the safe range, in range or above.
- The system needs to be able to "learn" a model from the historical data. This involves transforming the data into a special format (an "ARFF" file) and submitting this to the learning algorithm.
- The data-to-arff step needs to be flexible (i.e. able to be easily changed if the learner's data requirements change.
- Models will need to be persisted.
- The data needs to be reliably persisted.
Future requirements
- There may be a need to record other data for the patient, possibly temporally, such as diet, other drugs taken, smoking and alcohol consumption.
Initial design
The high level design: