Hierarchical Model View Controller
From CSSEMediaWiki
(Difference between revisions)
Nelson Shaw (Talk | contribs) (New page: Hierarchical Model View Controller (HMVC) is an extension on the traditional Model view controller (MVC) architecture. It's main purpose is for use in web applications. The HMVC came a...) |
Nelson Shaw (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
* Re-usability - By nature of the design it is easy to reuse nearly every piece of code. | * Re-usability - By nature of the design it is easy to reuse nearly every piece of code. | ||
* Extendibility - Makes the application more extensible without sacrificing ease of maintenance. | * Extendibility - Makes the application more extensible without sacrificing ease of maintenance. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| Line 19: | Line 16: | ||
*[[Observer]] | *[[Observer]] | ||
*[[Model view controller]] | *[[Model view controller]] | ||
| − | *[[ | + | *[[Presentation abstraction control]] |
Revision as of 08:55, 18 October 2010
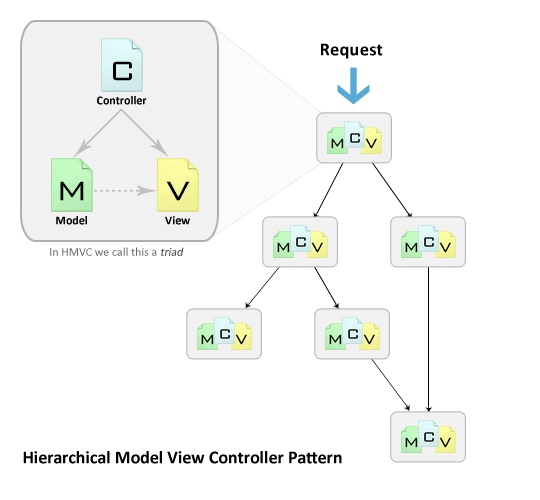
Hierarchical Model View Controller (HMVC) is an extension on the traditional Model view controller (MVC) architecture. It's main purpose is for use in web applications. The HMVC came about as a solution to scalability problems present in applications which used MVC. The solution was to convert the standard MVC into a hierarchy of parent child MVC layers.
Each MVC subgroup (triad) is independent from one another, but can communicate via their controllers. This allows for the software to be distributed over multiple locations.
Advantages of HMVC
- Modularization - Reduction of dependencies between the disparate parts of the application.
- Organization - Having a folder for each of the relevant triads makes for a lighter work load.
- Re-usability - By nature of the design it is easy to reuse nearly every piece of code.
- Extendibility - Makes the application more extensible without sacrificing ease of maintenance.