Adapter
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
There are two kinds: | There are two kinds: | ||
| − | * Object adapter: makes use of a toolkit/library class to implement its functionality | + | * Object adapter: makes use of a toolkit/library class to implement its functionality. |
| − | * Class-based adapter: uses multiple inheritance to make use of another superclass's functionality | + | * Class-based adapter: uses multiple inheritance to make use of another superclass's functionality. However Riel says we should [[Avoid multiple inheritance]]. |
== Use when == | == Use when == | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
From Gang of Four Design Patterns book: | From Gang of Four Design Patterns book: | ||
| − | Class based: | + | '''Class based:''' |
[[image: AdapterStructureClass.png]] | [[image: AdapterStructureClass.png]] | ||
| − | Object based: | + | '''Object based:''' |
[[image: AdapterStructureObject.png]] | [[image: AdapterStructureObject.png]] | ||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
[[image: AdapterExample.png]] | [[image: AdapterExample.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | In this example we have a drawing editor with an editable Shape object that can draw iteself. Implementing the Line subclass is reasonably simple, however if we need to display and edit text with the TextShape class it can be a lot harder to implement, and we may wish to use an existing toolkit called TextView. The problem is that TextView wasn't designed for the Shape class, so we need to adapt the interface without modifying the TextView toolkit (even if the toolkit was open source it would not make sense to modify a toolkit for one domain specific application). | ||
| + | |||
| + | The solution is to make TextShape an Adapter class, in this example we use the object adapter solution. Shapes boundingBox() requests are converted to the TextViews getExtent() request by TextShape. This allows the DrawingEditor to use the TextView class. | ||
| + | |||
| + | TextShape is also responsible for functionality that TextView doesn't provide. The diagram shows how TextShape implements the createManipulator() method of Shape. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == See also == | ||
| + | * [[Design patterns]] | ||
Revision as of 00:36, 7 October 2008
Adapter allows classes with incompatible interfaces work together, by converting the interface of one class into a form that a client expects. Basically you create an Adapter class as a go between to convert messages from one interface to another.
There are two kinds:
- Object adapter: makes use of a toolkit/library class to implement its functionality.
- Class-based adapter: uses multiple inheritance to make use of another superclass's functionality. However Riel says we should Avoid multiple inheritance.
Contents |
Use when
- You have an existing class (eg toolkit or library), but its interface doesn't fit in with your system
- You want to create a reusable class that cooperates with unrelated or unforeseen classes
- Object adapter only: You need to use several existing subclasses, but you don't want to adapt their interface by subclassing each one. Object adapters can adapt the interface of the parent class.
Structure
From Gang of Four Design Patterns book:
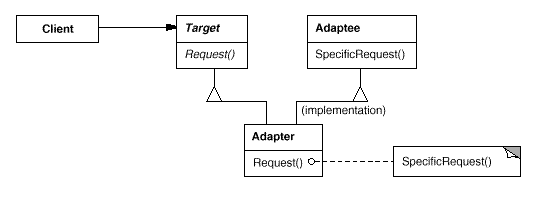
Class based:
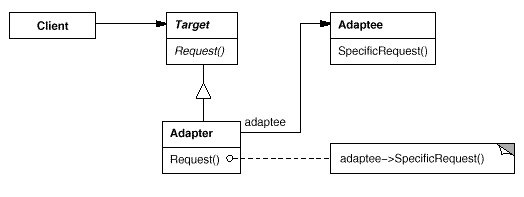
Object based:
Target
- Defines domain specific interface that a Client uses
Client
- Collaborates with objects that implement the Target interface
Adaptee
- An existing interface that needs adapting
Adapter
- Adapts the interface of Adaptee to the Target interface
Clients call operations on an Adapter object. The Adapter calls Adaptee operations to carry out the request.
Example
From the Gang of Four Design Patterns book:
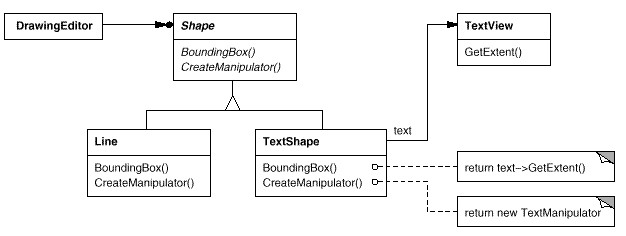
In this example we have a drawing editor with an editable Shape object that can draw iteself. Implementing the Line subclass is reasonably simple, however if we need to display and edit text with the TextShape class it can be a lot harder to implement, and we may wish to use an existing toolkit called TextView. The problem is that TextView wasn't designed for the Shape class, so we need to adapt the interface without modifying the TextView toolkit (even if the toolkit was open source it would not make sense to modify a toolkit for one domain specific application).
The solution is to make TextShape an Adapter class, in this example we use the object adapter solution. Shapes boundingBox() requests are converted to the TextViews getExtent() request by TextShape. This allows the DrawingEditor to use the TextView class.
TextShape is also responsible for functionality that TextView doesn't provide. The diagram shows how TextShape implements the createManipulator() method of Shape.