Template Method
Contents |
Intent
To allow the skeleton of an algorithm to be defined in a superclass, so that subclasses can redefine certain steps (methods/operations) of the algorithm as they see fit without changing the structure of the algorithm. The algorithm (template method) is defined in the superclass as abstract methods/operations in a fixed order.
When to use it
The template method should be used:
- To implement the parts of an algorithm that are fixed, and let the subclasses implement the behaviour in their own way.
- To refactor common subclass behaviour into the superclass to avoid code duplication.
- (There is a 3rd point in the Gang of Four Design Patterns book, but I don't understand it. Could anyone explain it here?)
Example
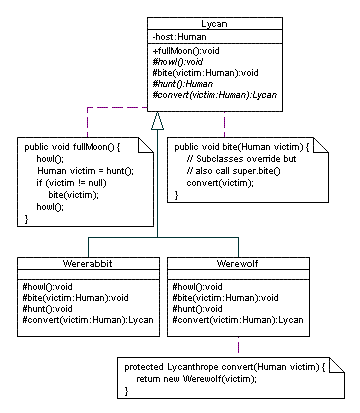
An example of a template method is the fullMoon() method of the Lycan class in our Monsters design. Here is the relevant part of the diagram:
The fullMoon() method in the Lycan class is the template method. As you can see the fullMoon() method is an algorithm that calls the howl(), hunt(), bite() and howl() methods in a specific order - these are the operations. The subclasses Wererabbit and Werewolf redefine the howl(), hunt() and bite() operations to do the specific actions for their type of class.
Important: note that the template method relies on the fundamental object oriented idea of Polymorphism. That is, even if we send the fullMoon() message to a Lycan variable which is actually a Werewolf object, the Werewolf's fullMoon() method will be the one that is actually called, and hence the operation methods of the Werewolf class will be used.
Recognising the pattern
Classes: AbstractClass, multiple ConcreteClasses
- templateMethod() that defines a skeleton of abstract protected method(s) in AbstractClass.
- AbstractClass has at least one subclass ConcreteClass.
- ConcreteClasses must implement all protected methods.