Matthew's Design Study
For my design study, I am going to be working to improve the design of my COSC460 project. The project is a plug-in for Eclipse designed to provide a tool for visualising software metrics directly onto source code. The plug-in is written in Java and is approximately 5K LOC.
Contents |
Desired Behaviour & Requirements
To be completed...
Existing Code Base
This system is my first attempt at developing this system. At first glance it appears fairly logical; however, some more serious OOD issues lurk beneath the surface...
Design Discussion/Overview
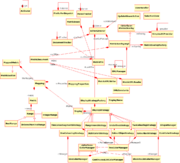
In this section I will briefly discuss each of the current components and their roles. Please note that these functional groupings do not directly correspond to existing packages. The diagrams to the left provide further detail.
- Plugin: This Singleton class provides a launcher for the Eclipse plugin. It provides all of the initial driving calls to instantiate the underlying document monitor and listeners.
- Document Monitor: This package provides handling of Java files in the editor, keeping track of those that have been loaded and also as a location to retrieve updated metrics data. Generally, this class relies on Singletons to keep track of the open files.
- Editor Listeners: These classes listen to the Eclipse editor, in most cases this is effectively the current document's buffer. Each change of state is reported to the EditorListener class.
- The Model: This set of packages provides a representation of the stored data. A MetricDocument contains all of the metrics, mappings and displays for a single Java file. There can be multiple
metrics represented using multiple mappings in any one document, and each of these may have multiple MetricSections, which represent the an actual appearance of the metric in the editor.
- Display & Editor Manipulation: This set of classes deal with the current Eclipse editor and provide the functionality to add adornments to the editor. A wide variety of these adornments exist,
they are backed up with appropriate Shape and Color managers.
- API: These classes provides an Observer interface where external 'Providers' can listen for and then as necessary provide metrics information as requested.
- Serialisation: This package allows metrics data to be provided and/or converted via a defined XML format.
- Eclipse View: These classes provide a view that allows users to alter which metric visualizations are currently active and which displays are being used for each.
Existing Usage of OOD Features & Techniques
- Design patterns currently used:
- Observer is used in the API.
- Singleton is used widely in both the Editor Listeners and the Document Monitor groupings.
- Strategy is used with the Display and DisplayStrategy.
- Command MetricFile acts like a passable object to facilitate interactions.
- Template Method is used in Range and Display Strategy.
- Factory Method is used in the API and with the Display.
- Design Maxims/Idioms followed (imo):
- Model the real world the classes represent solid concepts.
- Favor composition over inheritance composition is used in favor of inheritance where possible.
- Once and only once repeated code is minimal, even in the similar DisplayStrategy classes.
- ...
- Design Maixim/Idioms neglected:
- Behavioral completeness vs You ain't gonna need it neither of these principles have been explicitly followed.
- Extensibility has not been considered to a sufficient degree.
- Encapsulate that which varies has been broken as Strings are used to convey data in certain parts of the system.
- ...
Areas of Greatest Concern
- API: Is the architectural model appropriate? Is the use of the Observer pattern correct here? Maybe the MVC should be explored...
- Model: Are there any possible improvements?
- String Manipulation: Is there any way to avoid the current String manipulation in Mapping Properties?
- Display Strategies: Is there any way of simplifying this hierarchy? Are the current methods of instantiation appropriate?
- Eclipse View: Dynamic updating of data is a concern here.
- File Instances: Is the current design the most sound way of dealing with Eclipse's editor model (i.e. multiple files, with multiple views).
- Alternative Languages: What can be done to make the system more modular and appropriate for multiple languages?
First Design
Architecture
The key point to note here is that, if we consider the MVC pattern, the old architecture is clearly wrong as the provider of the Model is being told to update itself rather than informing the View when it is updated. This clearly breaks Tell, Don't Ask and a number of other significant maxims. In order to complete this transformation, the existing single Eclipse plugin will be broken into 3+ or more eclipse plug-ins with defined extension points and dependencies. This alteration will also have a significant affect on the API of the MetricsOverlay plugin.
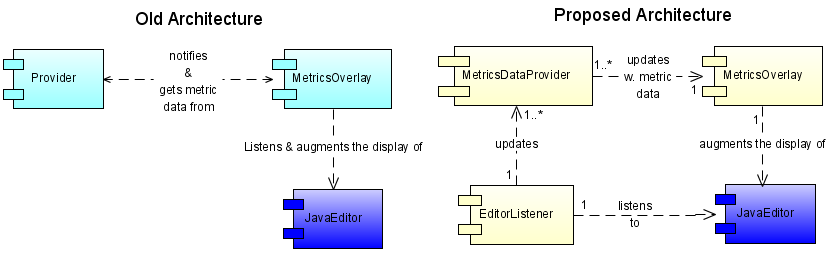
EditorListener component
This new plug-in responds to changes in Eclipse by listening to provided listener classes and collating all listen events.
Design Overview
- Activator - Provides the plug in instantiation.
- ServiceChecker - Checks available services that can provide dispatches and attaches dispatches as possible.
- Dispatch + Sublasses - These hierarchy checks Eclipse's hierarchy and listens to the available listeners to generate updates as appropriate, ie if the file type is right etc. Updates are call an appropriate method in EdiotrListener.
- EditorListener - Forms a part of an Observer pattern providing updates for any registered objects. Constructs an UpdatedEditor object to transfer during a update notification. This object keeps track of the previous state and uses this, with the incoming updates to determine the current state of the editor part that is currently active. If an update is needed, this class notifies any observers. This class also makes sure the ServiceTracker keeps up to date.
- UpdatedEditor - This data class stores the necessary information for accessing and modifying the editor.
- EditorState - This enum represents the state of the current editor. There are only 3 states we are actually interested in.
- AcceptableFileTypeHandler - This class allows the system to change the file types it is interested in. (Note: the default constructor is designed specifically for Java as this is its primary design. This should be subclassed for the Java version).
Comparison to Initial Design
New Features:
- Now abstracted to new plug in.
- Listens to a much wider variety of events.
- Can handle different file types.
Class Comparison:
- Editor Listener and FileBufferDispatch existed with mostly the same job. Editor listener is now much less complicated as it only produces results from the listening.
- Other Listeners (Dipatch) are all new, as is the service checker.
- File handling is no longer completely statically defined as AcceptableFileypeHandler is new.
- Updated editor is a new type of data object.
Design Consideration
- Removing EditorListener from its previous plug in was a result of using Separation of concerns.
- Singleton on Activator, EditorListener, ServiceChecker, Two Dispatches.
- Observer with EditorListener as the concrete observable object.
- Unclear Mediator between EditorListener and ServiceChecker.
- Unclear Strategy between EditorListener and AcceptableFileTypeHandler.
Still ToDo
- Create an abstract superclass for AcceptableFileTypeHandler and sub class for Java/UserDefined. This will clean up that strategy pattern.