Overloading
From CSSEMediaWiki
Revision as of 23:11, 8 August 2009 by Matthew Harward (Talk | contribs)
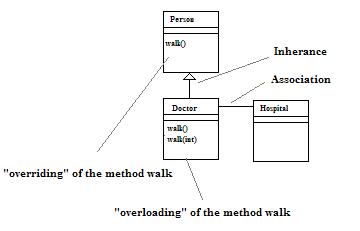
Overloading occurs when several methods have the same names with different method signatures. In the example above, the same method speak can have 2 different forms or method signatures. The first one only includes a single parameter word, the second one includes 2 parameters: word and language.
Overloading lets two functions/method share a name if they differ in the number and or the type of arguments; two functions may not differ only in their return type
| Nomenclature | |
|---|---|
| Techniques: Abstraction | Aggregation versus Composition | Association versus Dependency | Coupling | Encapsulation | Information hiding | Inheritance | Multiple Inheritance | Overloading | Polymorphism
Features: Abstract class | Class versus Object | Component versus Module | Instance | Interface | Method | Package versus Namespace | Superclass | Subclass | |