Introduce Null Object
BenMcDonald (Talk | contribs) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | [[Category:Design Patterns]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Behavioural Patterns]] | ||
''Summarised from Refactoring'' [[Martin Fowler 1999]] | ''Summarised from Refactoring'' [[Martin Fowler 1999]] | ||
| − | == | + | == Use When == |
If you have repeated checks for a null reference, because one can't invoke anything on a null reference. | If you have repeated checks for a null reference, because one can't invoke anything on a null reference. | ||
| Line 14: | Line 16: | ||
This pattern can also be used to act as a stub for testing if a certain feature, such as a database, is not available for testing. | This pattern can also be used to act as a stub for testing if a certain feature, such as a database, is not available for testing. | ||
| − | == | + | == Structure == |
Replace your check for a null reference with a null object | Replace your check for a null reference with a null object | ||
| Line 27: | Line 29: | ||
It can be regarded as a special case of the [[State pattern]] and the [[Strategy Pattern]]. | It can be regarded as a special case of the [[State pattern]] and the [[Strategy Pattern]]. | ||
| − | == | + | == Consequences == |
This neglates the need to check for a null reference. | This neglates the need to check for a null reference. | ||
Another advantage of this approach over a working default implementation is that a null object is predictable and has no side effects: it does nothing. | Another advantage of this approach over a working default implementation is that a null object is predictable and has no side effects: it does nothing. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Related Patterns== | ||
| + | [[Strategy]] | ||
| + | [[State]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{design patterns}} | ||
Revision as of 22:18, 2 August 2009
Summarised from Refactoring Martin Fowler 1999
Contents |
Use When
If you have repeated checks for a null reference, because one can't invoke anything on a null reference.
For example your code looks like:
if (customer == null) plan = BillingPlan.basic(); else plan = customer.getPlan();
This pattern can also be used to act as a stub for testing if a certain feature, such as a database, is not available for testing.
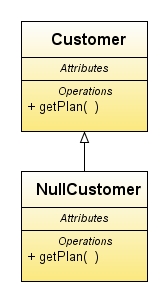
Structure
Replace your check for a null reference with a null object
- Create a subclass that acts as a null version of the class.
- Create an isNull() method in both classes. For the superclass it should return "false", and "true" for the subclass.
- Find all places that can give out a null value when asked for an object of the superclass and replace them to give a null object instead.
- Find all places that compare a variable of the superclass type with null and replace them with a call to isNull().
It can be regarded as a special case of the State pattern and the Strategy Pattern.
Consequences
This neglates the need to check for a null reference.
Another advantage of this approach over a working default implementation is that a null object is predictable and has no side effects: it does nothing.
Related Patterns
| Design patterns | |
|---|---|
|
Creational: Abstract Factory | Builder | Factory Method | Prototype | Singleton | |