Model view controller
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
The '''Model View Controller (MVC)''' is one of the oldest architectural patterns. It is still widely used in web and application programming. | The '''Model View Controller (MVC)''' is one of the oldest architectural patterns. It is still widely used in web and application programming. | ||
| − | The general premise is to separate application into three distinct parts: | + | The general premise is to separate an application into three distinct parts: |
* '''Model:''' The underlying model of the data, this is often provided by a back-end database. | * '''Model:''' The underlying model of the data, this is often provided by a back-end database. | ||
* '''View:''' The interface with the web client/browser or the application's GUI. | * '''View:''' The interface with the web client/browser or the application's GUI. | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
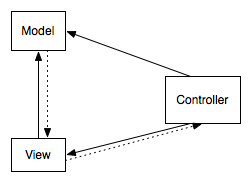
The MVC is often considered circular in form, with the model providing data for the view, which uses the controller to update the model. However, in some situations the controller is thought to sit between the view and the model. | The MVC is often considered circular in form, with the model providing data for the view, which uses the controller to update the model. However, in some situations the controller is thought to sit between the view and the model. | ||
| − | [[Ward's wiki]] considers both of these options incorrect. The controller should simply exist to promote communication and validation between the model and the view. It should provide ways to change the view, either through direct calls or the use of an [[Observer]]. Controversy exists on whether the MVC should be considered an OO design pattern at all. | + | [[Ward's wiki]] considers both of these options incorrect [http://www.c2.com/cgi/wiki?ModelViewController]. The controller should simply exist to promote communication and validation between the model and the view. It should provide ways to change the view, either through direct calls or the use of an [[Observer]]. Controversy exists on whether the MVC should be considered an OO design pattern at all. |
== Patterns == | == Patterns == | ||
| + | So, lets consider the variations of MVC. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === MVC-Observer-Strategy === | ||
[[Image:MVCDiagram.png|none|frame|Diagram from lecture 27/7/09]] | [[Image:MVCDiagram.png|none|frame|Diagram from lecture 27/7/09]] | ||
* '''Model''' and '''View''' resemble an [[Observer]]. | * '''Model''' and '''View''' resemble an [[Observer]]. | ||
* The '''Controller''' is a [[Strategy]]. | * The '''Controller''' is a [[Strategy]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === MVC-Mediator === | ||
| + | [[Image:MVCDiagram-Mediator.png|none|frame|Diagram from lecture 27/7/09]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''Controller''' resembles the [[Mediator]] between '''Model''' and '''View''' | ||
==External links== | ==External links== | ||
Revision as of 05:38, 30 July 2009
The Model View Controller (MVC) is one of the oldest architectural patterns. It is still widely used in web and application programming.
The general premise is to separate an application into three distinct parts:
- Model: The underlying model of the data, this is often provided by a back-end database.
- View: The interface with the web client/browser or the application's GUI.
- Controller: The logic (sometimes called 'business logic') that interfaces between the view and the model. In OO terms, the "controller offers facilities to change the state of the model."
The MVC is often considered circular in form, with the model providing data for the view, which uses the controller to update the model. However, in some situations the controller is thought to sit between the view and the model.
Ward's wiki considers both of these options incorrect [1]. The controller should simply exist to promote communication and validation between the model and the view. It should provide ways to change the view, either through direct calls or the use of an Observer. Controversy exists on whether the MVC should be considered an OO design pattern at all.
Contents |
Patterns
So, lets consider the variations of MVC.
MVC-Observer-Strategy
MVC-Mediator
- Controller resembles the Mediator between Model and View
External links
- Model View Controller - What Ward's wiki has to say about the MVC
- MVC's OO Nature - A discussion on Ward's wiki as to whether the MVC is appropriate or even valid for OOD.
- GUI Architectures by Martin Fowler